Long Term Effects Of Exercise (heart)
The effects long term sport has on the heart. If you do loads and loads of exercise your heart will get bigger because it can't take all the pressure that's being put on it and the heart can't take it, so in effect the heart can't handle being too fit. Your heart can only handle so much exercise. But your muscles get stronger.
Down below there is a picture of a heart, as mentioned already, if you do too much exercise, it will get bigger what thappens is that it will push one side of the heart more the other way, normally it's level. Therefore if your too fit it will push over to one side. That's what happens when you do long term exercise.
Your heart is a muscle and it gets thicker and then grows out, so that's how your heart gets bigger.
Your heart is a muscle and it gets thicker and then grows out, so that's how your heart gets bigger.
Long Term Effects Of Exercise (Muscles)
Your muscles get bigger when you do long term training because you are training them everyday, for like 6 hours a day. They are used to lifting all the weights so they will adjust to the weights. If you haven't been to the gym in ages and you lifted a big weight you would struggle to lift it the first time, it would take you a while, and you would have to do it a couple of times to exercise your muscles. As you exercise your muscles tear a little bit, and when you feel pain when you exercise that is you pushing your muscles to get bigger. They tear a little bit each time you exercise. Then they closeup after and that makes the muscle bigger
Long Term Effects Of Exercise (Respiration)
When you breathe old air is released from your lungs and fresh air travels into your lungs which then take in all the oxygen. You have two lungs but they are not the same size, the left lung is slightly smaller as it has to leave room for the heart. Oxygen from the air in your lungs is passed into the blood and this is pumped around your body by the heart. If you exercise your lungs have bigger capacity to allow more oxygen to get into the blood stream and this helps the blood flow around your body better to the muscles which in turn means your muscles have more oxygen for exercise.

Long Term Effects Of Exercise (Respiration)
When you breathe old air is released from your lungs and fresh air travels into your lungs which then take in all the oxygen. You have two lungs but they are not the same size, the left lung is slightly smaller as it has to leave room for the heart. Oxygen from the air in your lungs is passed into the blood and this is pumped around your body by the heart. If you exercise your lungs have bigger capacity to allow more oxygen to get into the blood stream and this helps the blood flow around your body better to the muscles which in turn means your muscles have more oxygen for exercise.

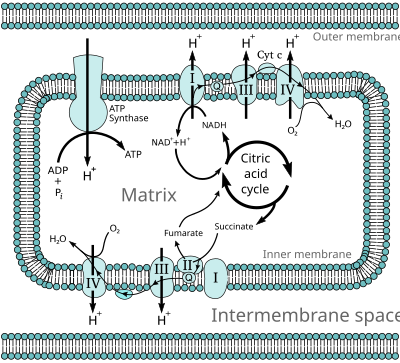
 ATP brakes down to make ADP and it relsese energy into are mucsles. The ATP energy only lasts up to 10 seconds
ATP brakes down to make ADP and it relsese energy into are mucsles. The ATP energy only lasts up to 10 seconds